Science Curriculum
at KCIS
The Primary Science curriculum is presented in four content areas: Scientific enquiry, Biology, Chemistry and Physics. Scientific enquiry is about considering ideas, evaluating evidence, planning investigative work and recording and analysing data. The Scientific enquiry objectives underpin Biology, Chemistry and Physics, which are focused on developing confidence and interest in scientific knowledge. Environmental awareness and some history of science are also incorporated. The Primary Science curriculum framework provides a solid foundation upon which the later stages of education can be built.

Grade 1-3
1
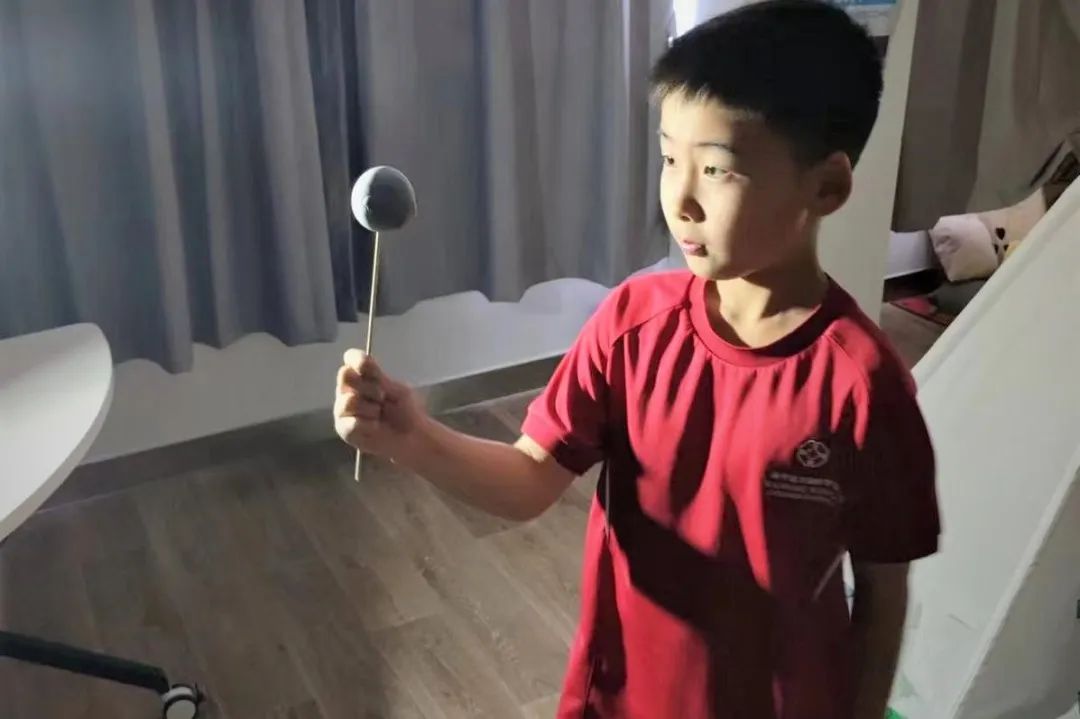
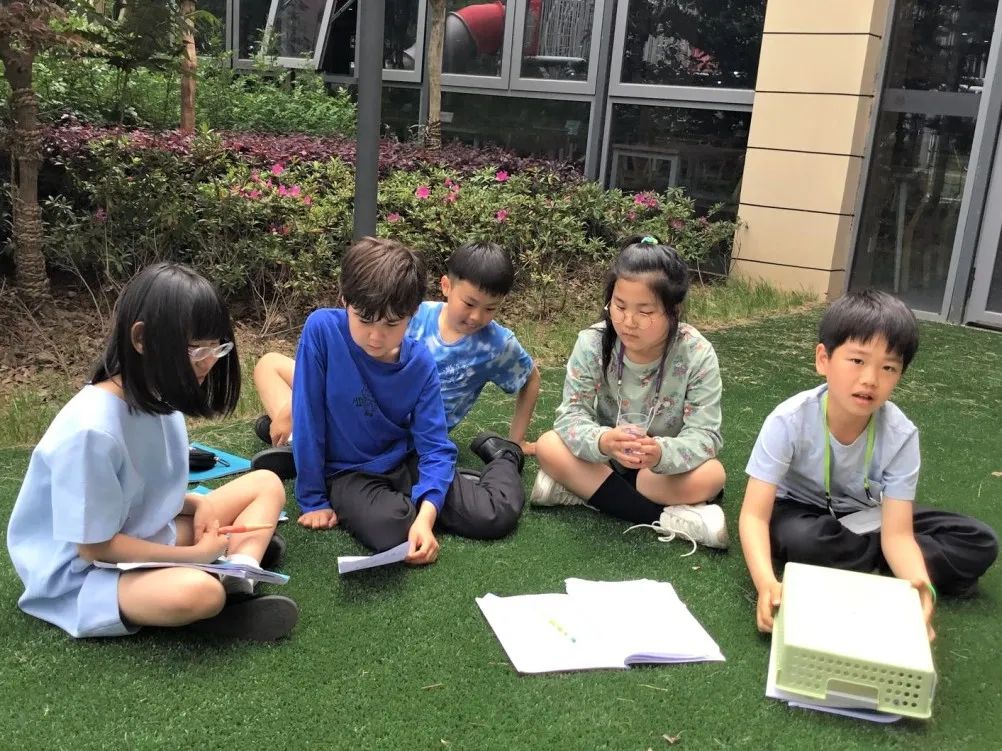


In Grade 1, students have been learning about living things in different places and making a change. They studied how different habitats contain many different species of plants and animals. They looked at the differences and similarities of plants and animals which live in different environments. Students learned how the direction and speed of an object can be altered by applying a force. They also looked at how a force can change the shape of an object and know how we can test an object to determine its properties.
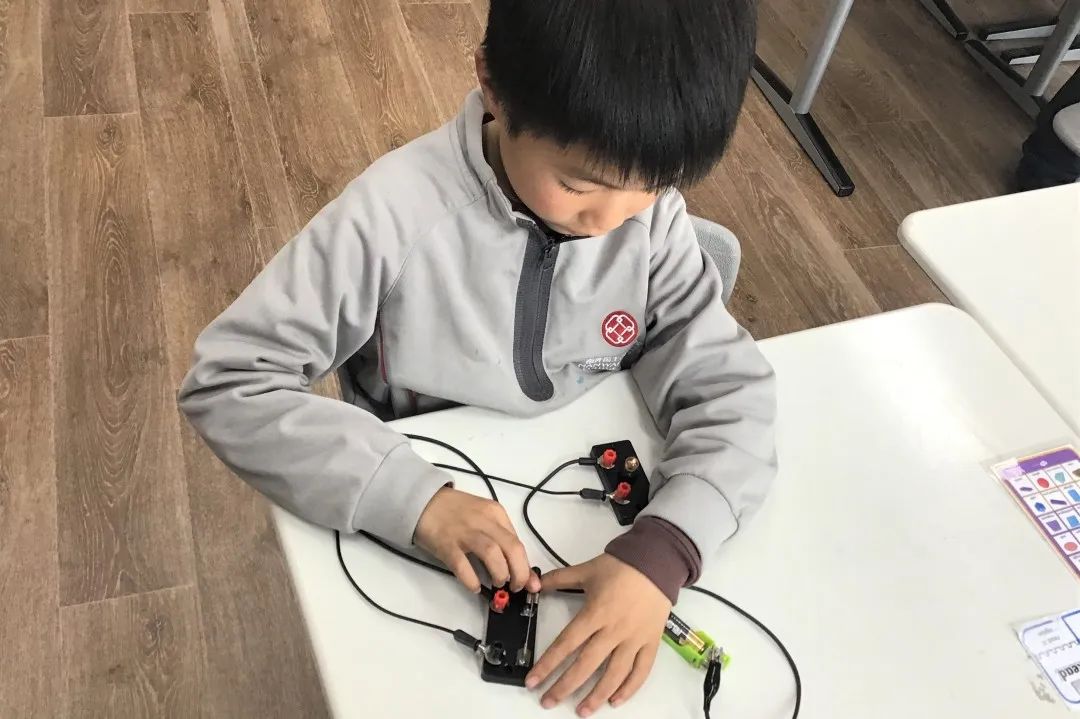
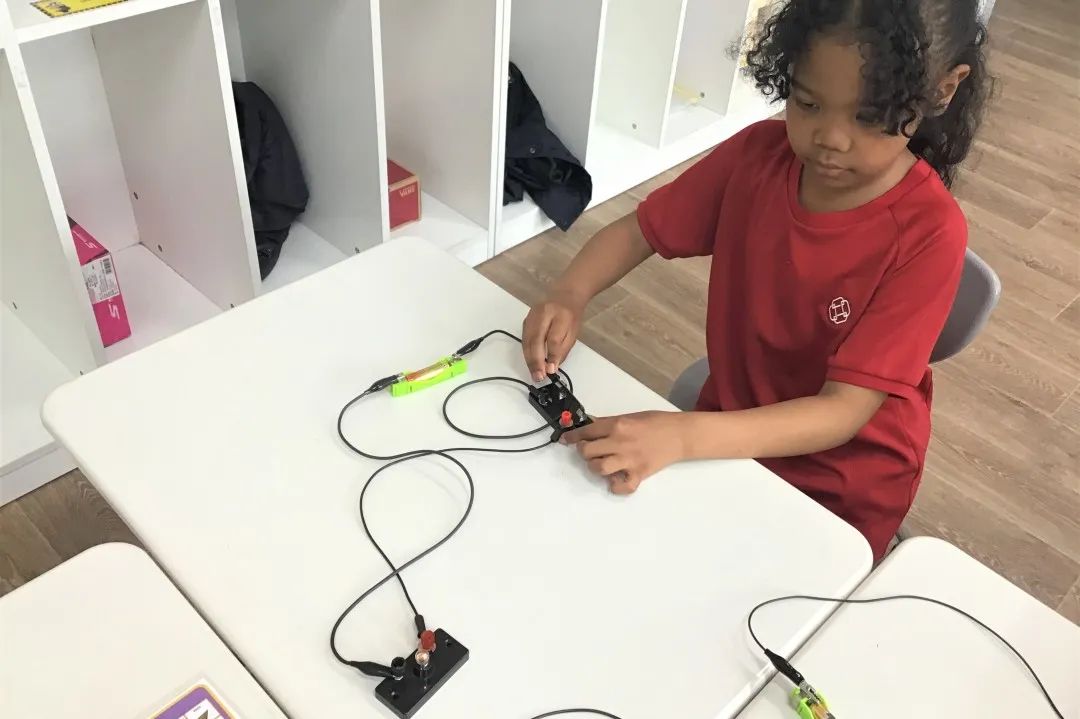
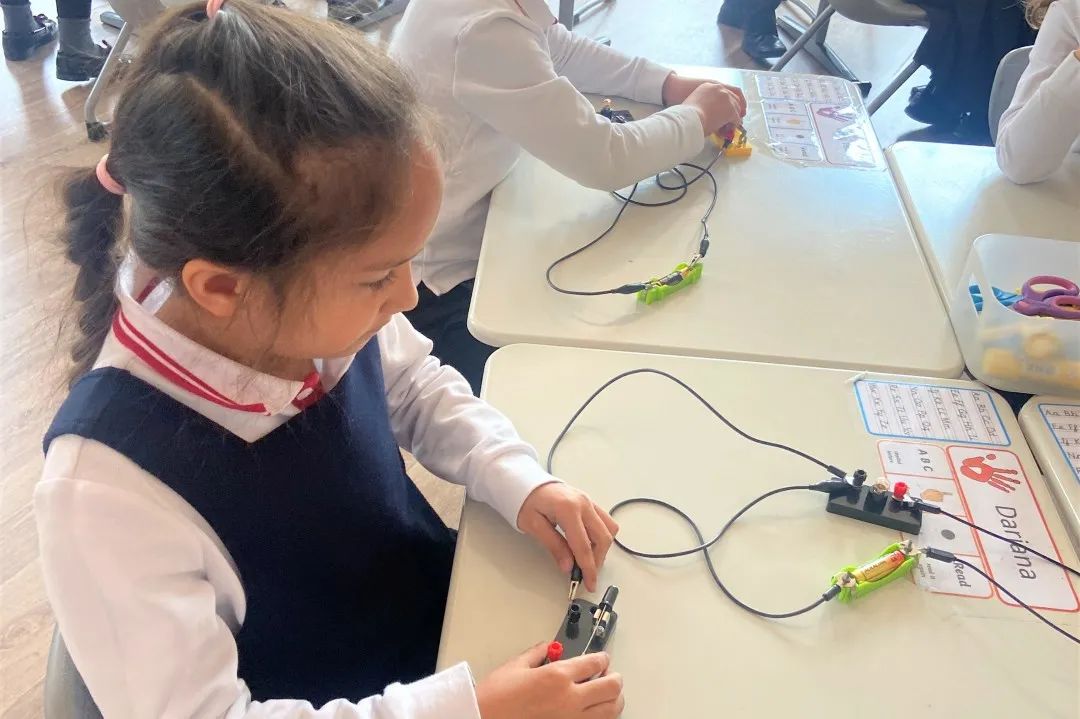
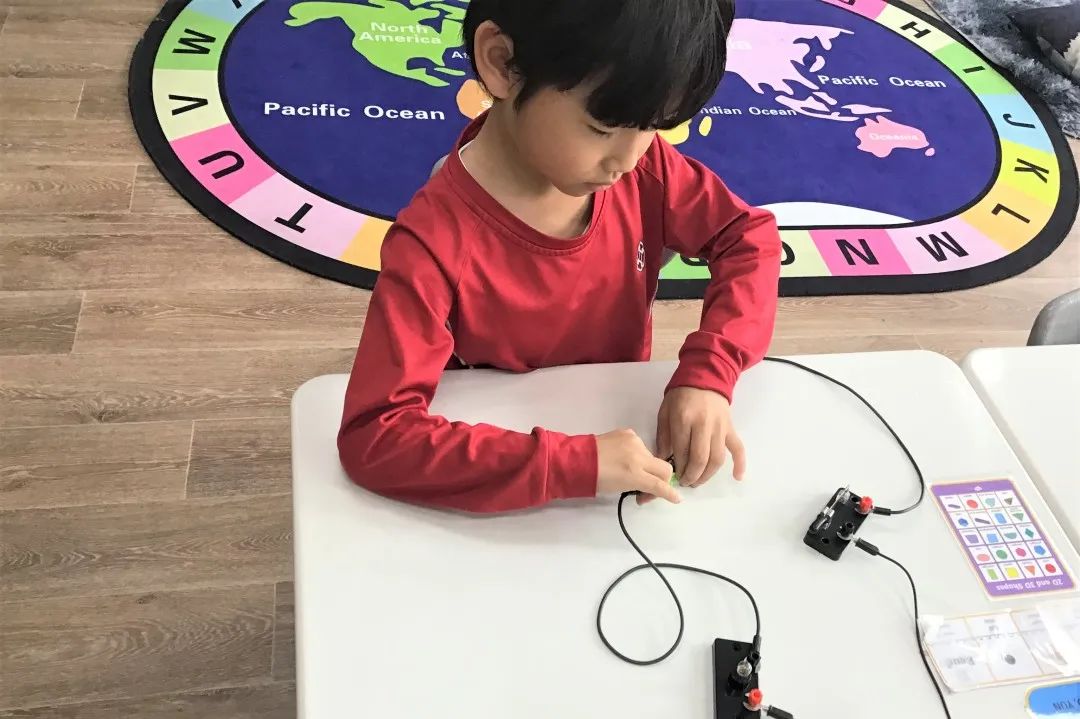




In Grade 2, students have been learning about animals including humans and forces. They studied the distinguishing features between mammals, fish, birds, insects, amphibians and reptiles. Students were able to compare how the offspring of different animals develop and grow. They identified some of the major organs in the human body and describe their function. They have looked at different forces including friction and how it makes moving objects more difficult. They have learned how to measure forces and describe how different surfaces have different friction.
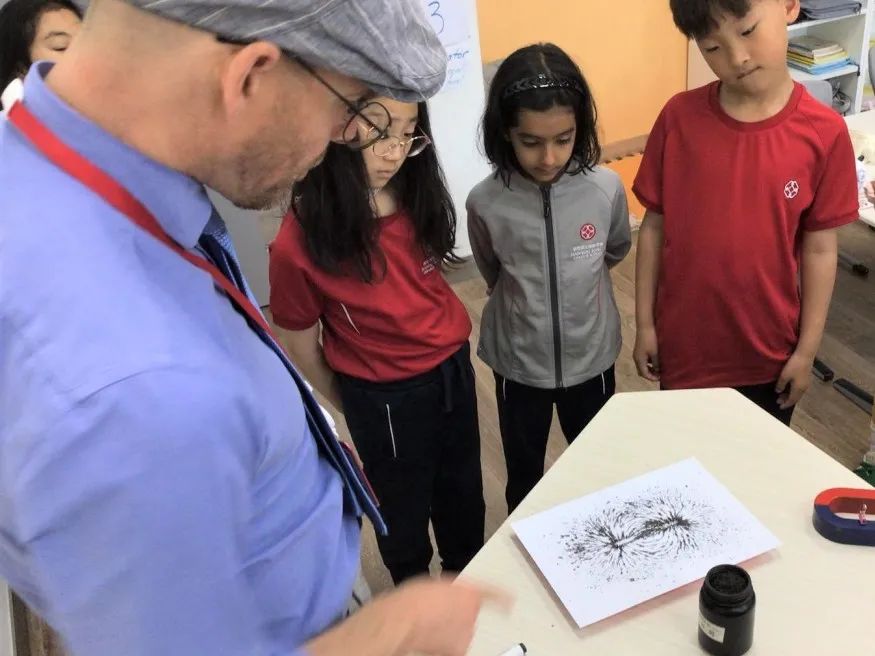

In Grade 3,
students have been learning about life processes and ecosystems as well as material properties and change. They looked at the different kinds of organisms in an ecosystem and the relationship between them. They were able to construct simple food chains showing feeding relationships between organisms. Students were able to explain solids, liquids and gases using particle theory. They explained changes of using particle theory do describe the arrangement of the molecules.
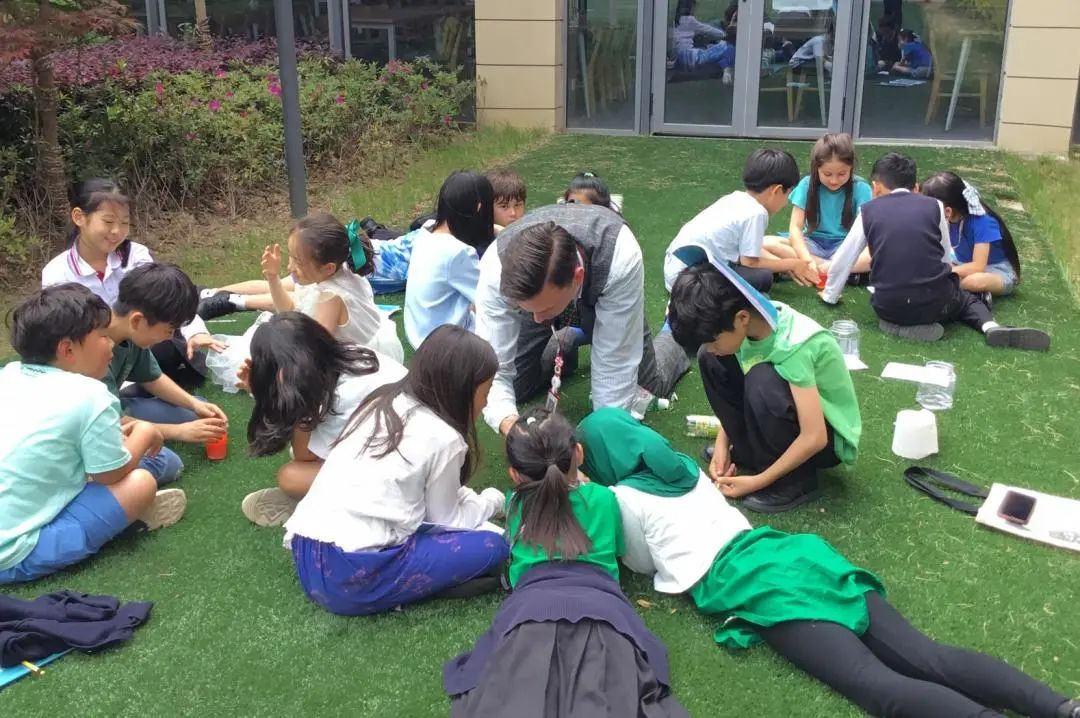
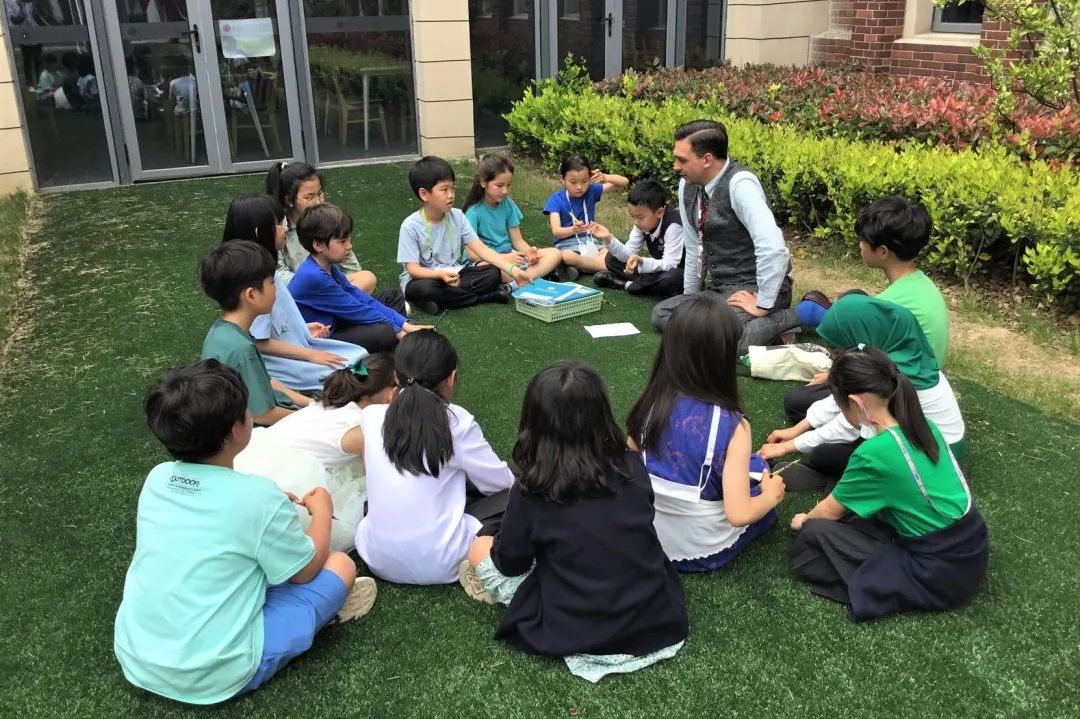
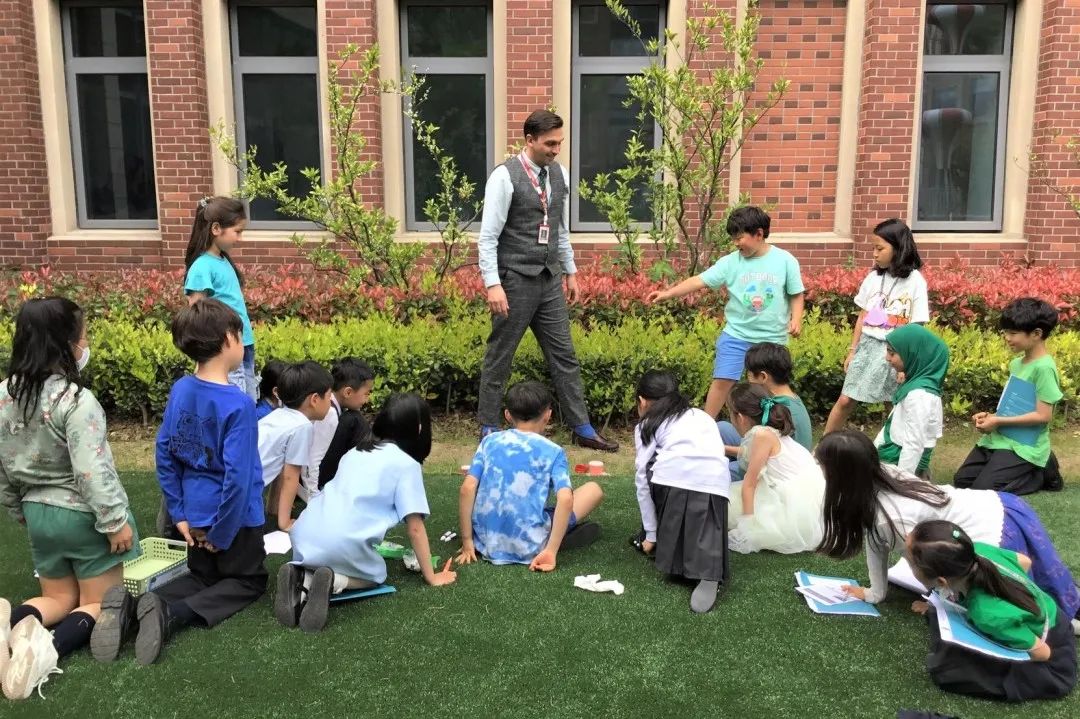
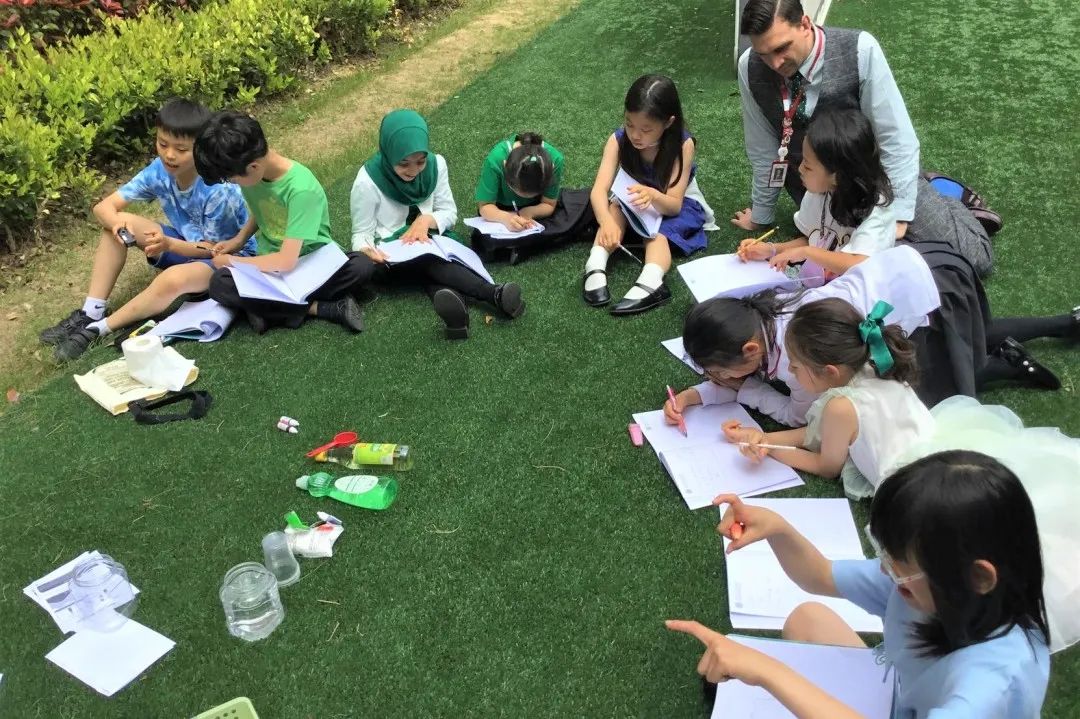






Grade 4-5
2
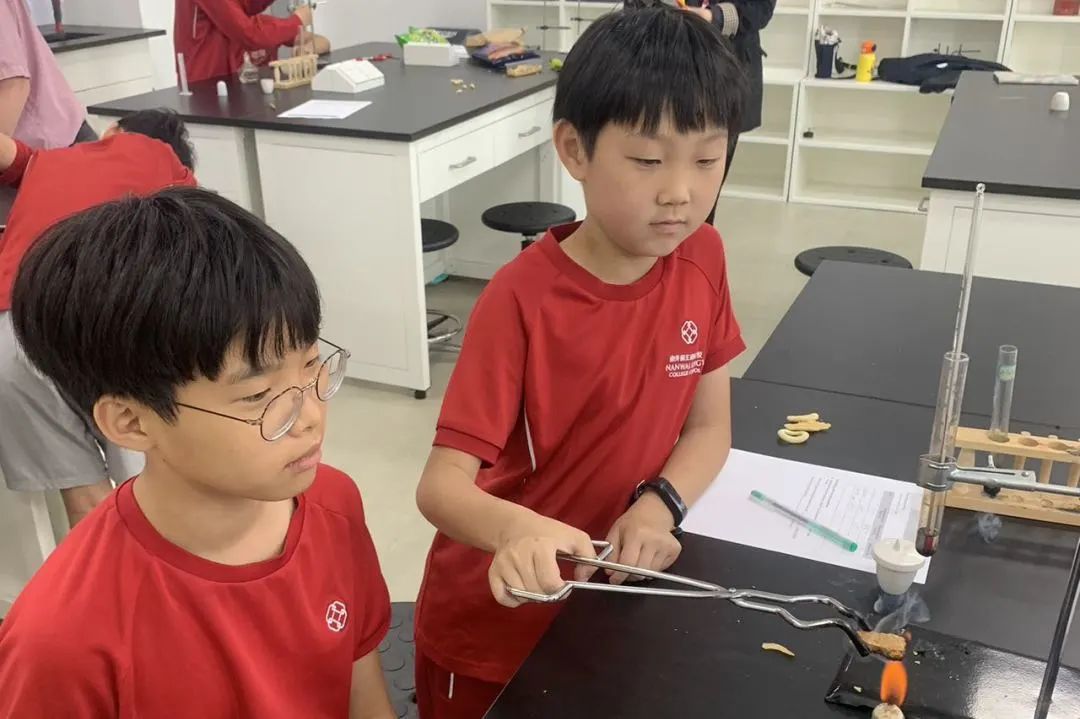
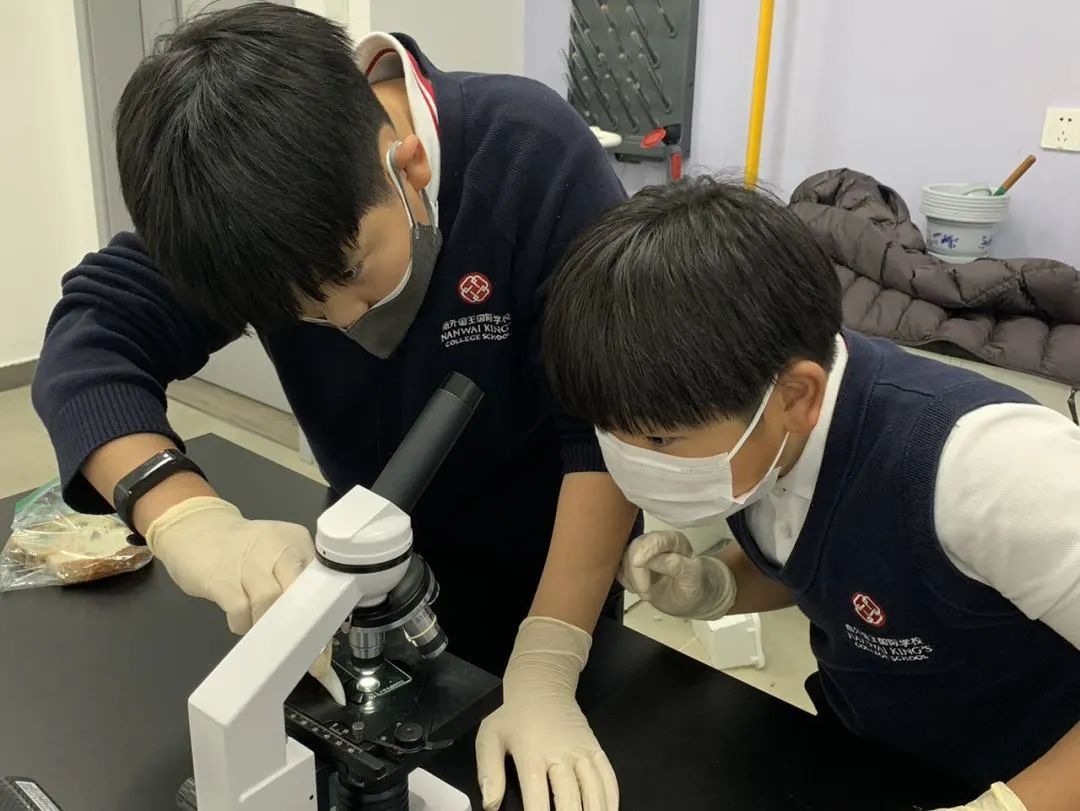


In Grade 4, students have been learning about the properties of materials and changes in materials. They described different properties of various materials and how we can group materials based on these properties. They were able to give reasons why we group materials in certain ways. Students explained the different states of matter and how we can change from one state to another. They looked at different mixtures and how some are reversible, and some are non-reversible.
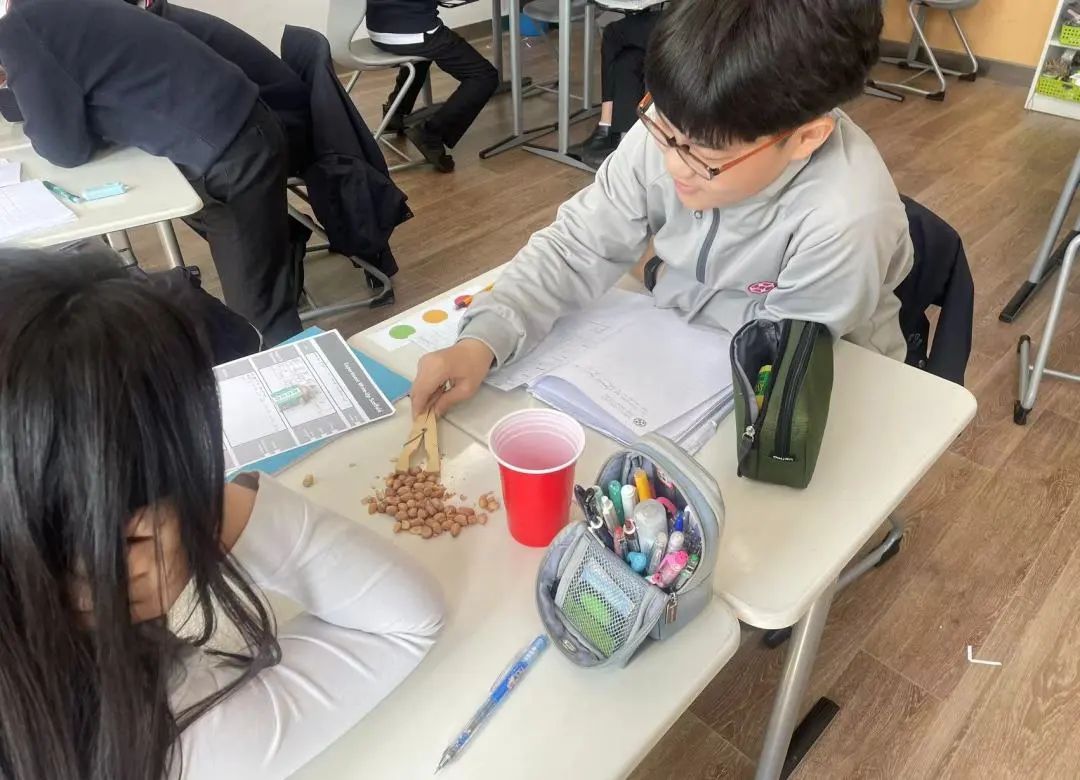
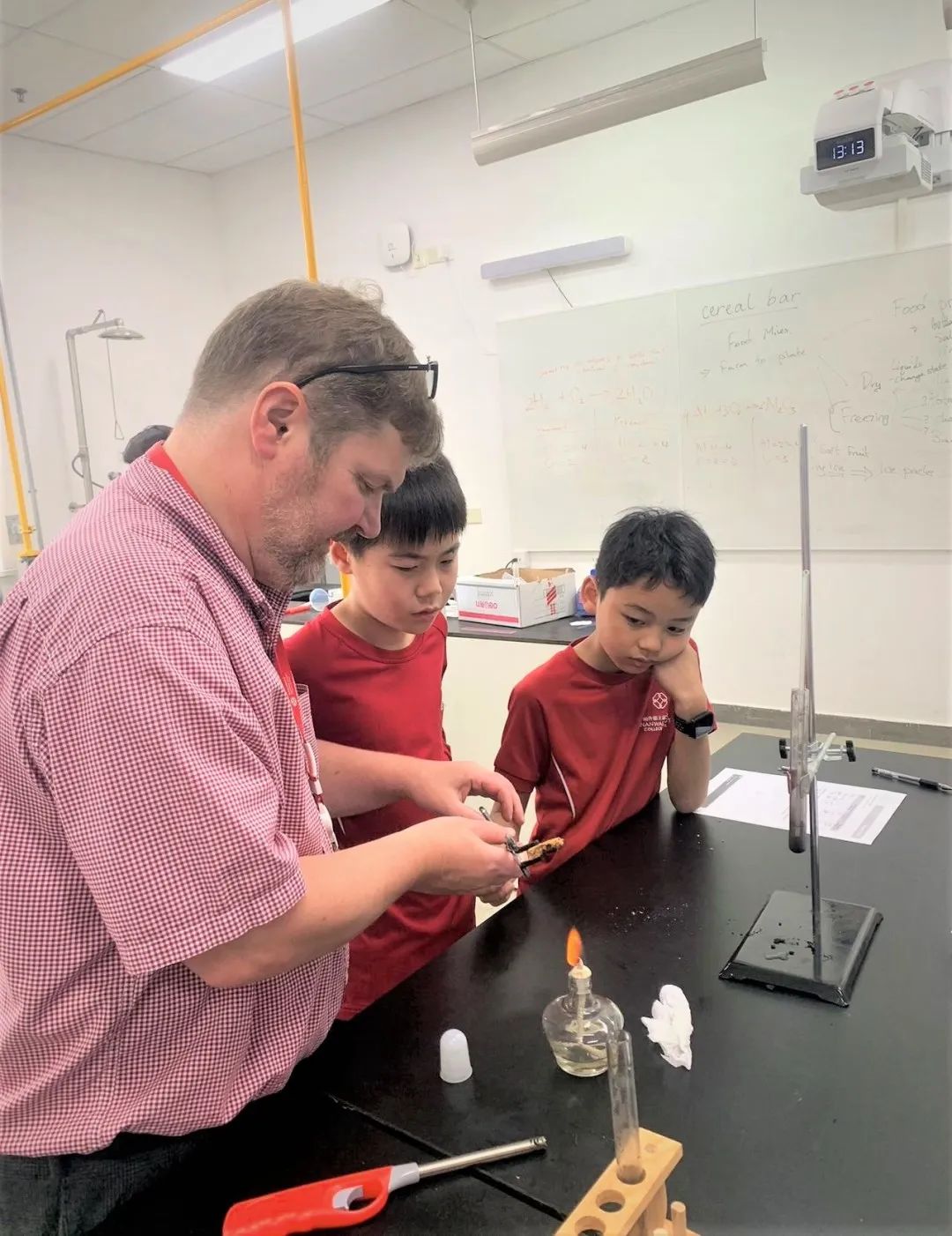
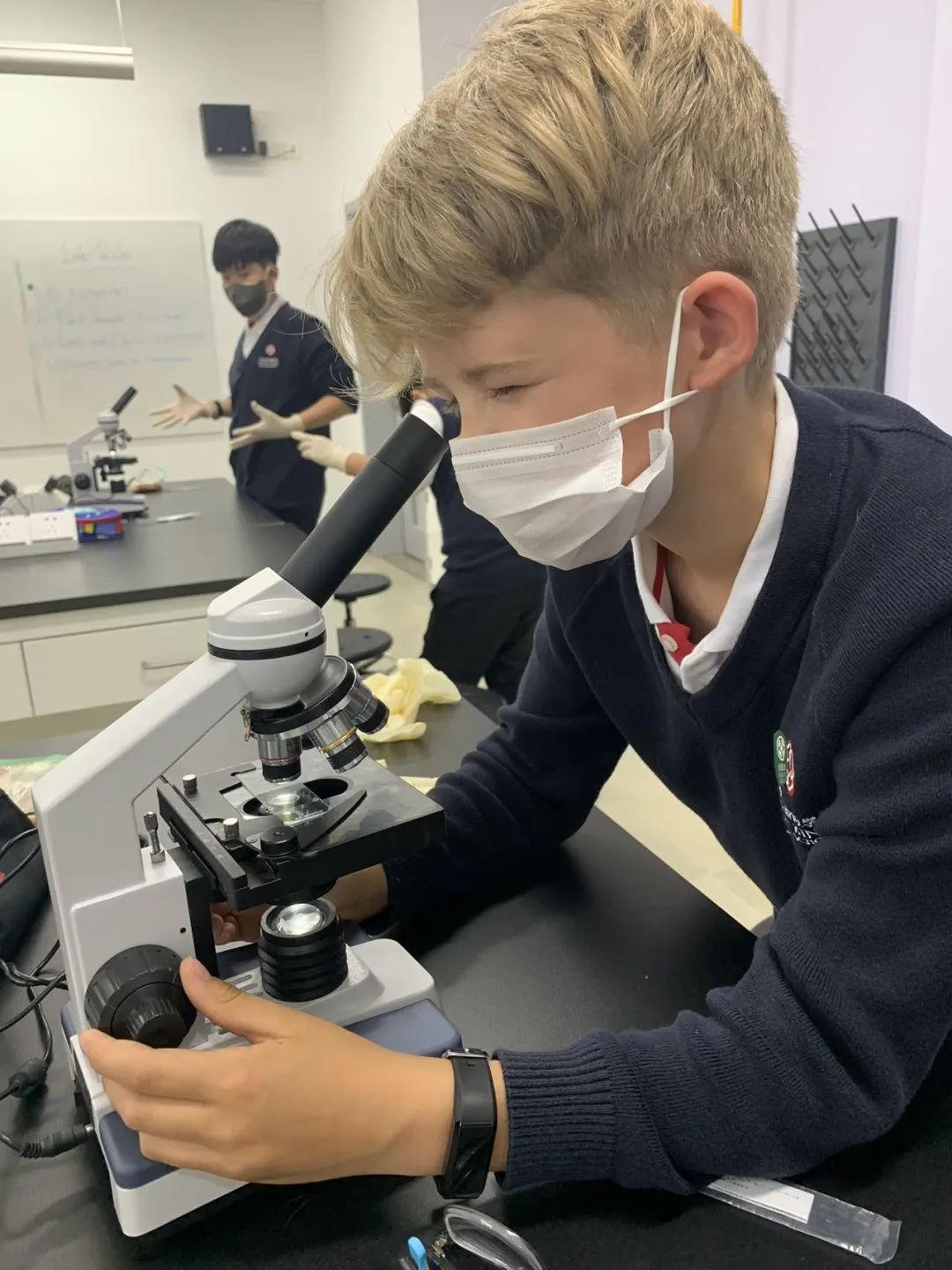
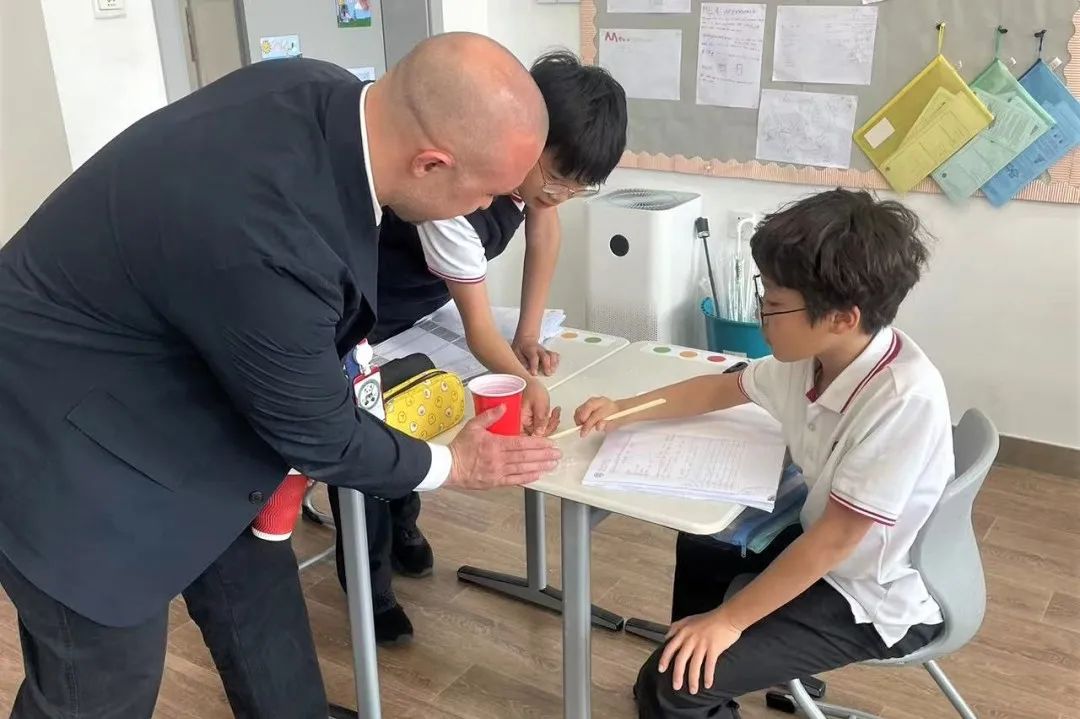




In Grade 5, the students have been learning about light and adaptations and evolution. They studied how light travels in straight lines and how shadows are formed. Students learned how light is reflected off surfaces and how to calculate the angle of reflection. They also used a prism to separate white light into different colours of the rainbow. Students examined how environments change over time and how organisms adapt to their environment. They analysed the advantages and disadvantages of these adaptations and how this has led to evolution of organisms.

Grade 6-8
3
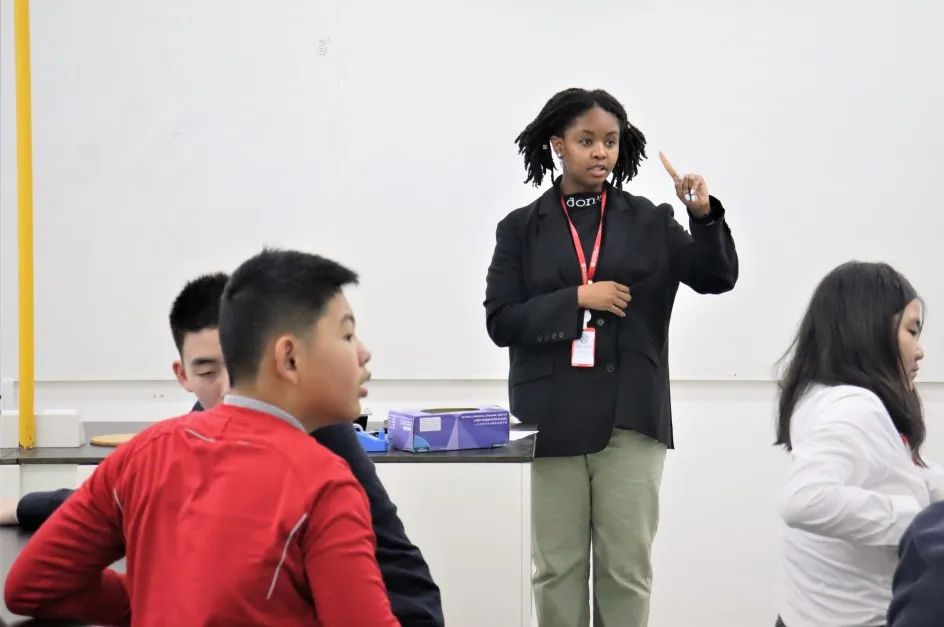
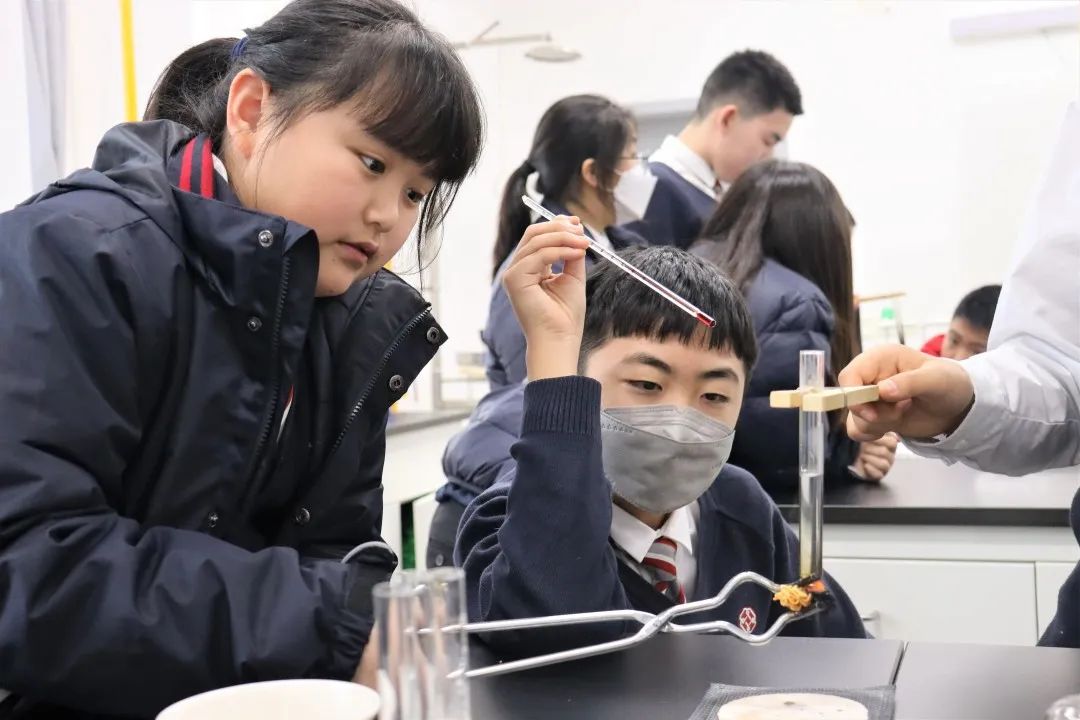



In Grade 6, the students have been learning about classifying life, explaining the properties of matter, energy and sound and the environment and the ecosystem. They have looked at how we classify organisms and using dichotomous keys to identify different organisms. Students studied chemical and physical properties of matter including acidity and alkalinity as well as the physical properties of metals and alloys. They studied how sound travels in waves and how the sound travels through the particles in the wave. Students looked at the structure of the earth and plate tectonics. They can describe how plate tectonics influences natural disasters such as volcanoes and earthquakes.
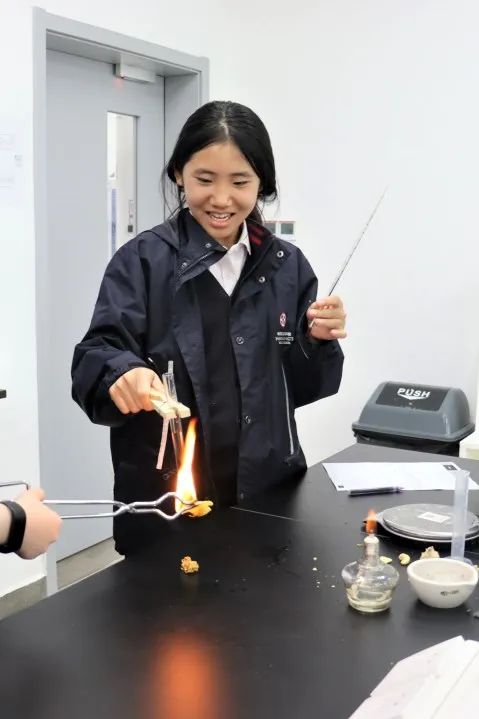
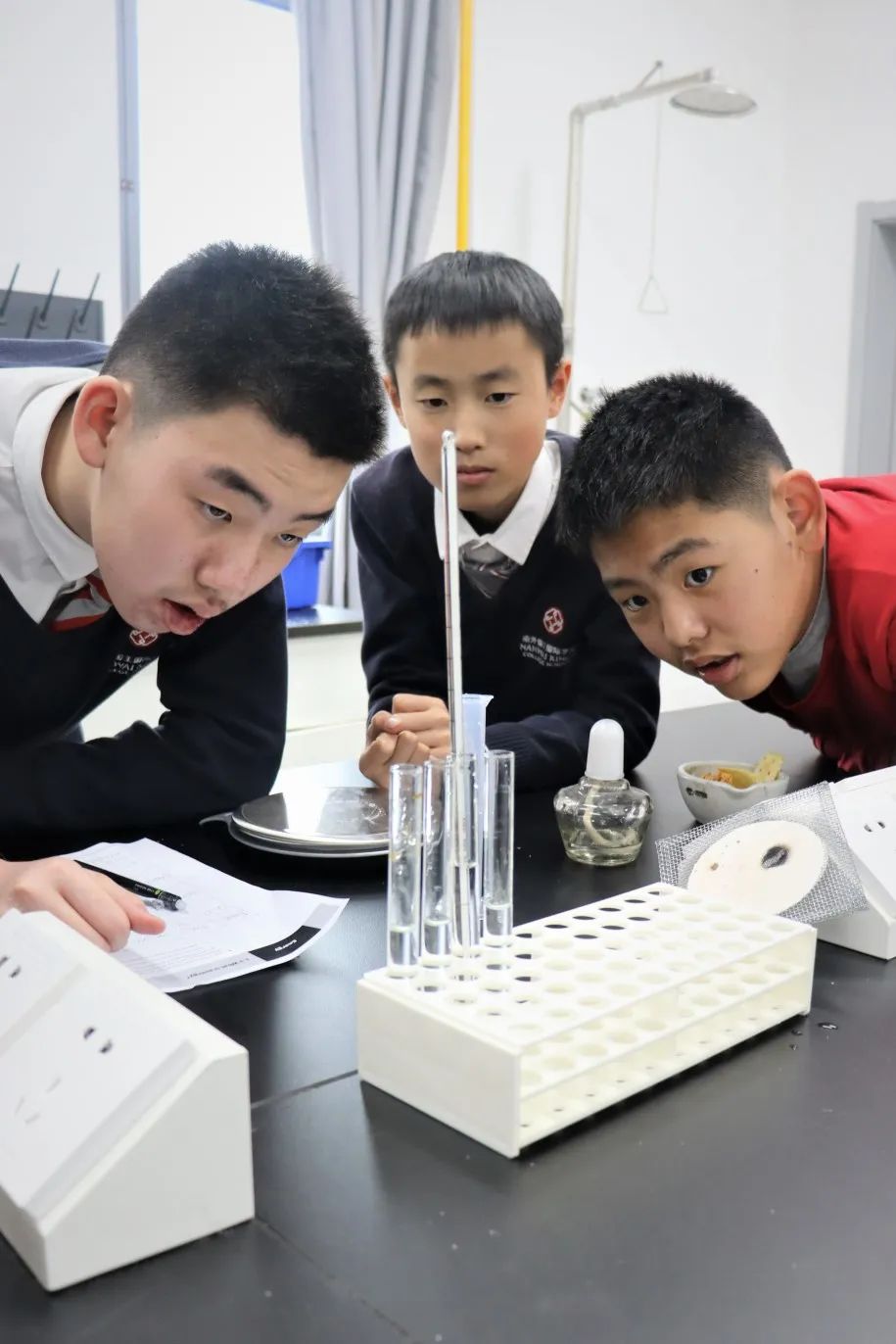


In Grade 7, the students have been learning about transport in plants and animals, metals and non-metals, sound and reproduction and growth. Students investigated how water is transported from the roots to the leaves of a plant and how environmental conditions affect the movemenent. They studied the heart and blood and investigated the relationship between the circulatory system and cellular respiration. They looked at the properties of metals and non-metals and investigated how we use certain materials for certain purposes based on these properties. They also investigated some chemical reactions of metals and how this can be seen in real life e.g.rusting. Students studied how sound travels in waves and were able to interpred the different parts of the wave e.g amplitude, frequency and pitch. They studied the reproductive system as well as fertilisation, fetal development and growth. They learned the physical changes that happen during adolescence and how growth and development can be affected by diet drugs and disease.
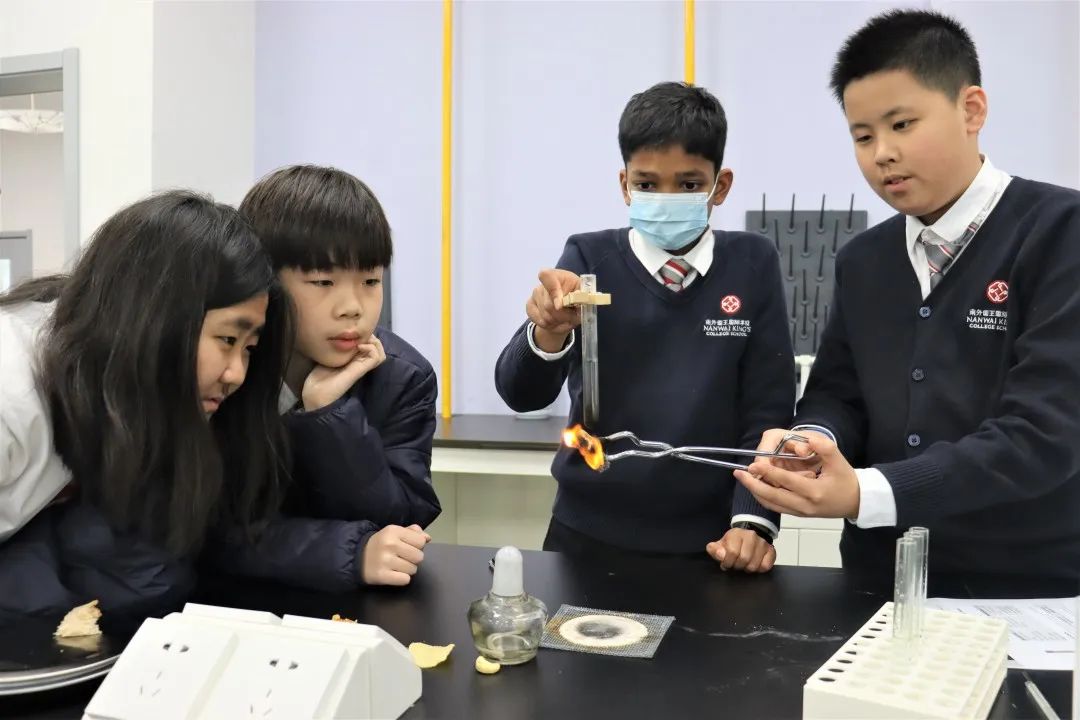
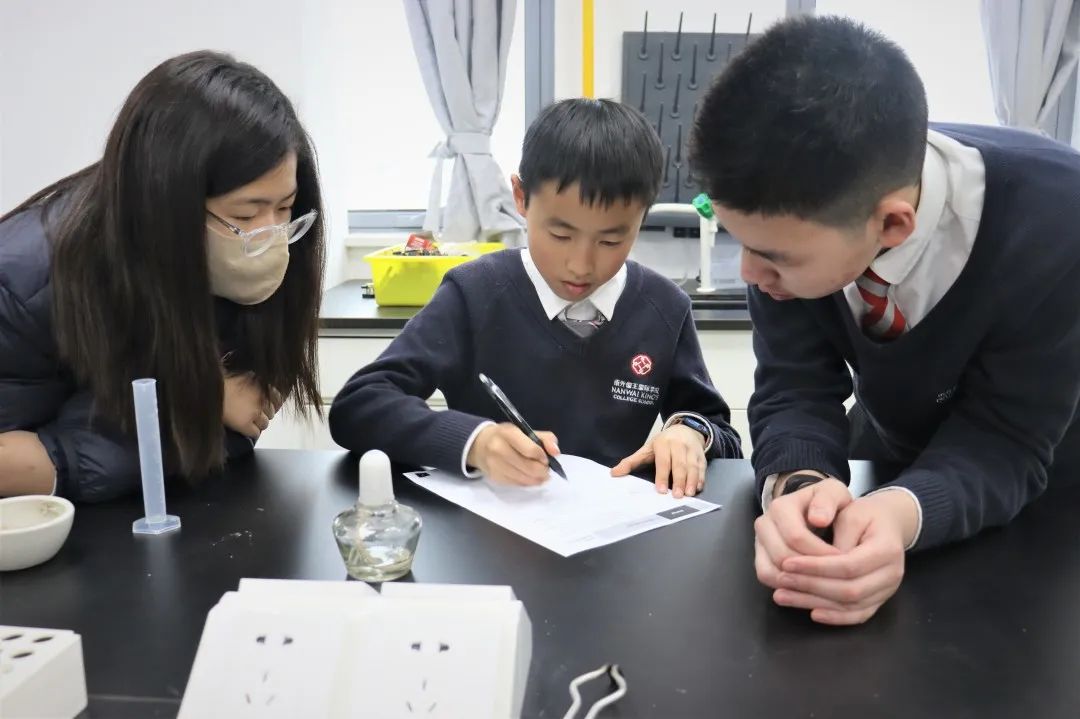


In Grade 8, students have been learning about reproduction in plants, rates of reaction, moments pressure and density and ecology. They looked at the different parts of a flower pollination, fertilisation development of the fruit and seed and seed dispersal. Students investigated the reaction of metals with oxygen, water and acids. They looked at the reactivity series and how the rate of reaction is affected by particle size, concentration, temperature and catalysts. Students investigated how to determine the densities of solids liquids and gases. They looked at how forces can cause objects to turn on a pivot and they understand the principle of moments. Students studied how pressure is the application of a force on a given area. They looked at ecosystems, how species are adapted to their environment and that they inherit characteristics from their parents. They looked at Darwins theories of natural selection and evolution. Students learned how to construct food chains and food webs and can explain the consequences of disease and extinction on these food chains.





 ENGLISH
ENGLISH 简体中文
简体中文

